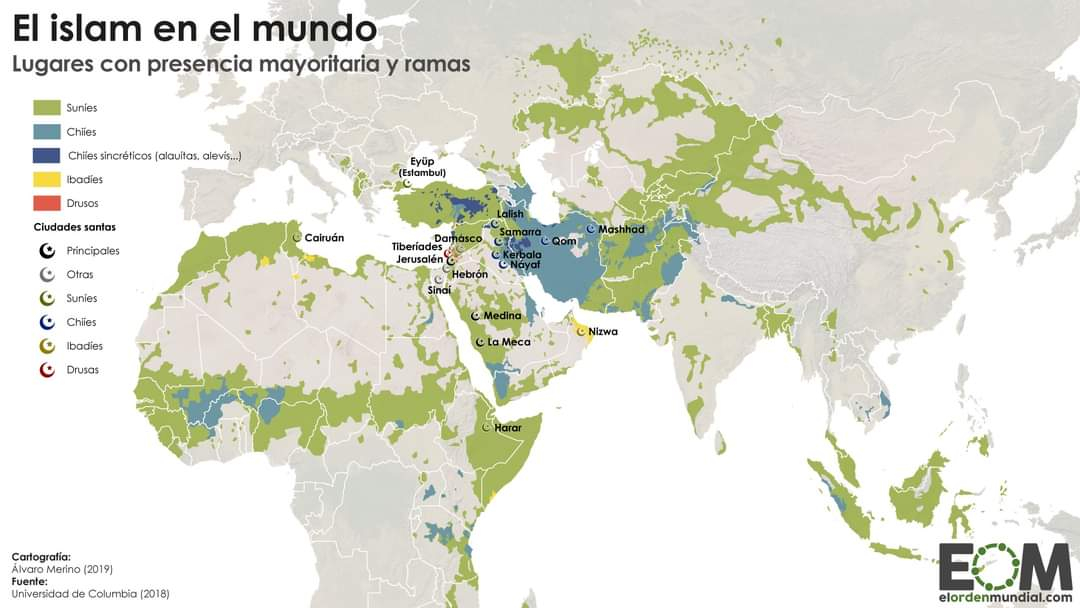
Islamic World
The Islamic world refers to countries and regions where Islam is dominant, influencing various aspects of life, including culture, politics, law, and education. It is not just limited to the Middle East; it spans Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Critical Aspects of the Islamic World:
1. Geographical Spread:
Middle East and North Africa (MENA): The heartland of Islam, including countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Iran, and Turkey.
South Asia: Countries like Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan, where Islam plays a central role.
Southeast Asia: Indonesia, the world's most populous Muslim-majority country, Malaysia, and Brunei.
Sub-Saharan Africa: Countries like Nigeria, Sudan, and Somalia have significant Muslim populations.
Europe: There are significant Muslim communities in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, and growing populations in Western Europe due to migration.
2. Cultural and Religious Practices:
Religious Practices: The Five Pillars of Islam (Shahada, Salah, Zakat, Sawm, Hajj) are central to Islamic life.
Islamic Law (Sharia): In many Muslim-majority countries, Sharia law influences or directly governs legal systems, covering everything from criminal law to personal status issues like marriage and inheritance.
Language: Arabic is the liturgical language of Islam, but other languages, such as Persian, Turkish, Urdu, and Malay, are widely spoken in the Islamic world.
3. Historical Contributions:
The Golden Age of Islam (8th to 14th century) was a period of significant advancements in science, medicine, mathematics, and philosophy, with learning centres in cities like Baghdad, Cairo, and Cordoba.
Architecture: Islamic architecture is renowned for its mosques, madrasas (schools), and palaces, featuring minarets, domes, and intricate geometric designs.
4. Modern-Day Dynamics:
Political Landscape: The Islamic world includes various governance systems, from monarchies in the Gulf States to republics in Iran and Turkey. Political Islam and movements like the Muslim Brotherhood have had significant influence in some regions.
Economic Power: The Islamic world includes some of the world's largest oil producers, like Saudi Arabia and Iran, which play a critical role in global energy markets.
Social Issues: The Islamic world faces diverse social challenges, from modernisation and globalisation to debates over women's rights, democracy, and the role of religion in the state.
5. Global Influence:
Diaspora: Significant Muslim communities in Europe, North America, and other parts of the world contribute to the global influence of Islam.
Interfaith Relations: Islam is one of the world's major religions, with interfaith dialogue becoming increasingly important in promoting understanding and cooperation between different religious communities.
The Islamic world is diverse and complex, with a rich history and significant impact on global culture, politics, and economics.
Islamic World
The Islamic world refers to countries and regions where Islam is dominant, influencing various aspects of life, including culture, politics, law, and education. It is not just limited to the Middle East; it spans Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Critical Aspects of the Islamic World:
1. Geographical Spread:
Middle East and North Africa (MENA): The heartland of Islam, including countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Iran, and Turkey.
South Asia: Countries like Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan, where Islam plays a central role.
Southeast Asia: Indonesia, the world's most populous Muslim-majority country, Malaysia, and Brunei.
Sub-Saharan Africa: Countries like Nigeria, Sudan, and Somalia have significant Muslim populations.
Europe: There are significant Muslim communities in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, and growing populations in Western Europe due to migration.
2. Cultural and Religious Practices:
Religious Practices: The Five Pillars of Islam (Shahada, Salah, Zakat, Sawm, Hajj) are central to Islamic life.
Islamic Law (Sharia): In many Muslim-majority countries, Sharia law influences or directly governs legal systems, covering everything from criminal law to personal status issues like marriage and inheritance.
Language: Arabic is the liturgical language of Islam, but other languages, such as Persian, Turkish, Urdu, and Malay, are widely spoken in the Islamic world.
3. Historical Contributions:
The Golden Age of Islam (8th to 14th century) was a period of significant advancements in science, medicine, mathematics, and philosophy, with learning centres in cities like Baghdad, Cairo, and Cordoba.
Architecture: Islamic architecture is renowned for its mosques, madrasas (schools), and palaces, featuring minarets, domes, and intricate geometric designs.
4. Modern-Day Dynamics:
Political Landscape: The Islamic world includes various governance systems, from monarchies in the Gulf States to republics in Iran and Turkey. Political Islam and movements like the Muslim Brotherhood have had significant influence in some regions.
Economic Power: The Islamic world includes some of the world's largest oil producers, like Saudi Arabia and Iran, which play a critical role in global energy markets.
Social Issues: The Islamic world faces diverse social challenges, from modernisation and globalisation to debates over women's rights, democracy, and the role of religion in the state.
5. Global Influence:
Diaspora: Significant Muslim communities in Europe, North America, and other parts of the world contribute to the global influence of Islam.
Interfaith Relations: Islam is one of the world's major religions, with interfaith dialogue becoming increasingly important in promoting understanding and cooperation between different religious communities.
The Islamic world is diverse and complex, with a rich history and significant impact on global culture, politics, and economics.