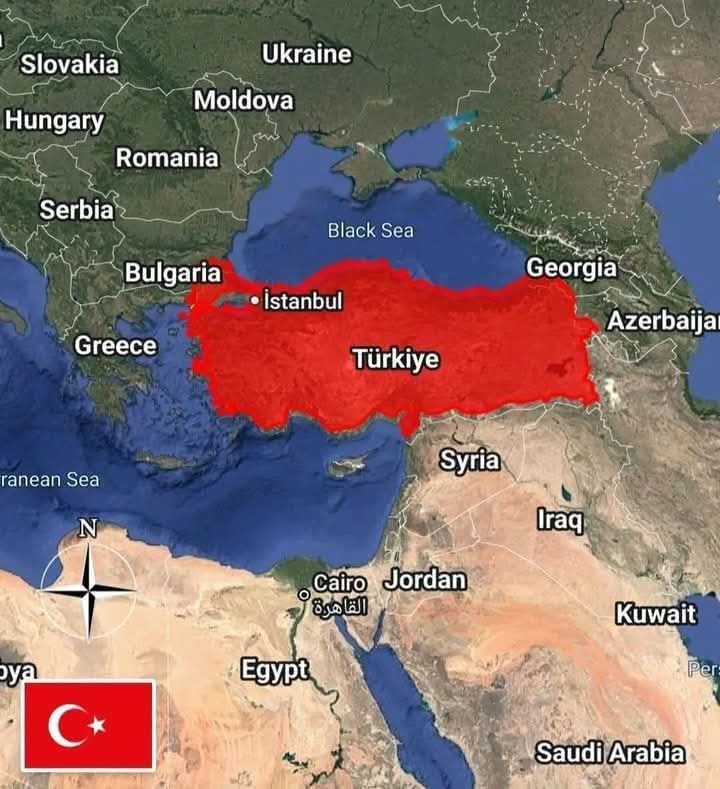
#Turkey is a country located at the crossroads of *two continents*, *Asia* and *Europe*, giving it a unique strategic position. Turkey is rich in culture and history, being home to many ancient civilizations, including the *Ottoman Empire* and the *Byzantine Empire*. It is known for its diverse geography, including beautiful *beaches*, towering *mountains*, and amazing archaeological sites. Turkey is also one of the world's major tourist destinations.
25 Facts About Turkey:
*1. Geographic Location*
Turkey is located at the crossroads of *Asia* and *Europe*.
*2. Capital*
The capital is *Ankara*, while *Istanbul* is the largest and most famous city.
*3. Area*
Turkey covers an area of about *783,356 km²*, making it one of the largest countries in the world.
*4. Population*
Turkey's population is approximately *85 million people* in 2024.
*5. Official Language*
The official language is *Turkish*.
*6. Religion*
The primary religion in Turkey is *Islam*, with the majority being *Sunni Muslims*.
*7. Government*
Turkey is a *democratic republic* with a *presidential system*.
*8. Currency*
The official currency is the *Turkish Lira (TRY)*.
*9. Climate*Turkey has a diverse climate: a *Mediterranean climate* on the coast and a *continental climate* in the inland areas.
*10. Terrain*
Turkey has varied terrain, including *mountains*, *plains*, and *rivers*.
*11. Highest Peak*
The highest peak in Turkey is *Mount Ararat* (Ağrı Dağı), with an elevation of *5,137 meters*.
*12. Tourism*
Turkey is one of the most popular tourist destinations, attracting about *40 million tourists annually*.
*13. Tourist Attractions*
Turkey has many famous tourist sites, such as *Hagia Sophia* in *Istanbul*, the *Bodrum Mausoleum*, and *Cappadocia*.
*14. Long History*
Turkey is home to ancient civilizations such as the *Ottoman Empire*, the *Byzantine Empire*, the *Greeks*, and the *Romans*.
*15. Historical Significance*
The city of *Istanbul* was the capital of both the *Byzantine Empire* and the *Ottoman Empire*.
*16. Turkish Cuisine*
Turkish cuisine is world-famous, with dishes like *kebab*, *hummus*, *baklava*, and *meze*.
*17. Sports*
*Football* is the most popular sport in Turkey, along with *basketball* and *water sports*.
*18. Turkish Culture*
Turkey is a blend of *Eastern and Western* influences, reflecting its rich cultural heritage.
*19. Education*Turkey has a strong educational system, with well-known universities like *Boğaziçi University* and *Istanbul University*.
*20. Renewable Energy*
Turkey is investing in *renewable energy*, particularly in *solar* and *wind power*.
*21. Trade and Industry*
Turkey is a major commercial hub, exporting products such as *textiles*, *machinery*, and *agricultural products*.
*22. Islamic Culture*
Turkey has a rich Islamic history, with many famous *mosques* like the *Sultan Ahmed Mosque (Blue Mosque)*.
*23. Turkish Arts*
Turkey is known for its arts, including *calligraphy*, *Islamic decoration*, and *traditional dances*.
*24. Space and Astronomy*
Turkey is developing its own space program and aims to reach space in the coming years.
*25. Politics*
Turkey is a member of *NATO* and the *G20*, playing a key role in global politics.
Turkey is a country with a *long history* and *rich culture*, blending *ancient traditions* with modern developments, making it an exciting destination for tourists and investors alike.
C: Geographic
25 Facts About Turkey:
*1. Geographic Location*
Turkey is located at the crossroads of *Asia* and *Europe*.
*2. Capital*
The capital is *Ankara*, while *Istanbul* is the largest and most famous city.
*3. Area*
Turkey covers an area of about *783,356 km²*, making it one of the largest countries in the world.
*4. Population*
Turkey's population is approximately *85 million people* in 2024.
*5. Official Language*
The official language is *Turkish*.
*6. Religion*
The primary religion in Turkey is *Islam*, with the majority being *Sunni Muslims*.
*7. Government*
Turkey is a *democratic republic* with a *presidential system*.
*8. Currency*
The official currency is the *Turkish Lira (TRY)*.
*9. Climate*Turkey has a diverse climate: a *Mediterranean climate* on the coast and a *continental climate* in the inland areas.
*10. Terrain*
Turkey has varied terrain, including *mountains*, *plains*, and *rivers*.
*11. Highest Peak*
The highest peak in Turkey is *Mount Ararat* (Ağrı Dağı), with an elevation of *5,137 meters*.
*12. Tourism*
Turkey is one of the most popular tourist destinations, attracting about *40 million tourists annually*.
*13. Tourist Attractions*
Turkey has many famous tourist sites, such as *Hagia Sophia* in *Istanbul*, the *Bodrum Mausoleum*, and *Cappadocia*.
*14. Long History*
Turkey is home to ancient civilizations such as the *Ottoman Empire*, the *Byzantine Empire*, the *Greeks*, and the *Romans*.
*15. Historical Significance*
The city of *Istanbul* was the capital of both the *Byzantine Empire* and the *Ottoman Empire*.
*16. Turkish Cuisine*
Turkish cuisine is world-famous, with dishes like *kebab*, *hummus*, *baklava*, and *meze*.
*17. Sports*
*Football* is the most popular sport in Turkey, along with *basketball* and *water sports*.
*18. Turkish Culture*
Turkey is a blend of *Eastern and Western* influences, reflecting its rich cultural heritage.
*19. Education*Turkey has a strong educational system, with well-known universities like *Boğaziçi University* and *Istanbul University*.
*20. Renewable Energy*
Turkey is investing in *renewable energy*, particularly in *solar* and *wind power*.
*21. Trade and Industry*
Turkey is a major commercial hub, exporting products such as *textiles*, *machinery*, and *agricultural products*.
*22. Islamic Culture*
Turkey has a rich Islamic history, with many famous *mosques* like the *Sultan Ahmed Mosque (Blue Mosque)*.
*23. Turkish Arts*
Turkey is known for its arts, including *calligraphy*, *Islamic decoration*, and *traditional dances*.
*24. Space and Astronomy*
Turkey is developing its own space program and aims to reach space in the coming years.
*25. Politics*
Turkey is a member of *NATO* and the *G20*, playing a key role in global politics.
Turkey is a country with a *long history* and *rich culture*, blending *ancient traditions* with modern developments, making it an exciting destination for tourists and investors alike.
C: Geographic
#Turkey 🇹🇷 is a country located at the crossroads of *two continents*, *Asia* and *Europe*, giving it a unique strategic position. Turkey is rich in culture and history, being home to many ancient civilizations, including the *Ottoman Empire* and the *Byzantine Empire*. It is known for its diverse geography, including beautiful *beaches*, towering *mountains*, and amazing archaeological sites. Turkey is also one of the world's major tourist destinations.
25 Facts About Turkey:
🌐 *1. Geographic Location*
Turkey is located at the crossroads of *Asia* and *Europe*.
🌐 *2. Capital*
The capital is *Ankara*, while *Istanbul* is the largest and most famous city.
🌐 *3. Area*
Turkey covers an area of about *783,356 km²*, making it one of the largest countries in the world.
🌐 *4. Population*
Turkey's population is approximately *85 million people* in 2024.
🌐 *5. Official Language*
The official language is *Turkish*.
🌐 *6. Religion*
The primary religion in Turkey is *Islam*, with the majority being *Sunni Muslims*.
🌐 *7. Government*
Turkey is a *democratic republic* with a *presidential system*.
🌐 *8. Currency*
The official currency is the *Turkish Lira (TRY)*.
🌐 *9. Climate*Turkey has a diverse climate: a *Mediterranean climate* on the coast and a *continental climate* in the inland areas.
🌐 *10. Terrain*
Turkey has varied terrain, including *mountains*, *plains*, and *rivers*.
🌐 *11. Highest Peak*
The highest peak in Turkey is *Mount Ararat* (Ağrı Dağı), with an elevation of *5,137 meters*.
🌐 *12. Tourism*
Turkey is one of the most popular tourist destinations, attracting about *40 million tourists annually*.
🌐 *13. Tourist Attractions*
Turkey has many famous tourist sites, such as *Hagia Sophia* in *Istanbul*, the *Bodrum Mausoleum*, and *Cappadocia*.
🌐 *14. Long History*
Turkey is home to ancient civilizations such as the *Ottoman Empire*, the *Byzantine Empire*, the *Greeks*, and the *Romans*.
🌐 *15. Historical Significance*
The city of *Istanbul* was the capital of both the *Byzantine Empire* and the *Ottoman Empire*.
🌐 *16. Turkish Cuisine*
Turkish cuisine is world-famous, with dishes like *kebab*, *hummus*, *baklava*, and *meze*.
🌐 *17. Sports*
*Football* is the most popular sport in Turkey, along with *basketball* and *water sports*.
🌐 *18. Turkish Culture*
Turkey is a blend of *Eastern and Western* influences, reflecting its rich cultural heritage.
🌐 *19. Education*Turkey has a strong educational system, with well-known universities like *Boğaziçi University* and *Istanbul University*.
🌐 *20. Renewable Energy*
Turkey is investing in *renewable energy*, particularly in *solar* and *wind power*.
🌐 *21. Trade and Industry*
Turkey is a major commercial hub, exporting products such as *textiles*, *machinery*, and *agricultural products*.
🌐 *22. Islamic Culture*
Turkey has a rich Islamic history, with many famous *mosques* like the *Sultan Ahmed Mosque (Blue Mosque)*.
🌐 *23. Turkish Arts*
Turkey is known for its arts, including *calligraphy*, *Islamic decoration*, and *traditional dances*.
🌐 *24. Space and Astronomy*
Turkey is developing its own space program and aims to reach space in the coming years.
🌐 *25. Politics*
Turkey is a member of *NATO* and the *G20*, playing a key role in global politics.
Turkey is a country with a *long history* and *rich culture*, blending *ancient traditions* with modern developments, making it an exciting destination for tourists and investors alike.
C: Geographic
0 Comments
0 Shares